Major sectors of Vietnam's manufacturing industry (apparel, electronics, auto parts, etc.)
Vietnam Industry: Key Sectors Driving the Nation’s Manufacturing Growth
What are the major sectors of Vietnam's manufacturing industry driving its rapid growth? As the Vietnam industry strengthens its global presence, understanding these key areas is essential. The country's manufacturing landscape is shaped by vibrant industries like textiles, electronics, automotive, and supporting sectors such as furniture and food processing. Exploring these major sectors reveals why Vietnam continues to attract international investment and expand its role in global supply chains.
Overview of Vietnam's Manufacturing Industry
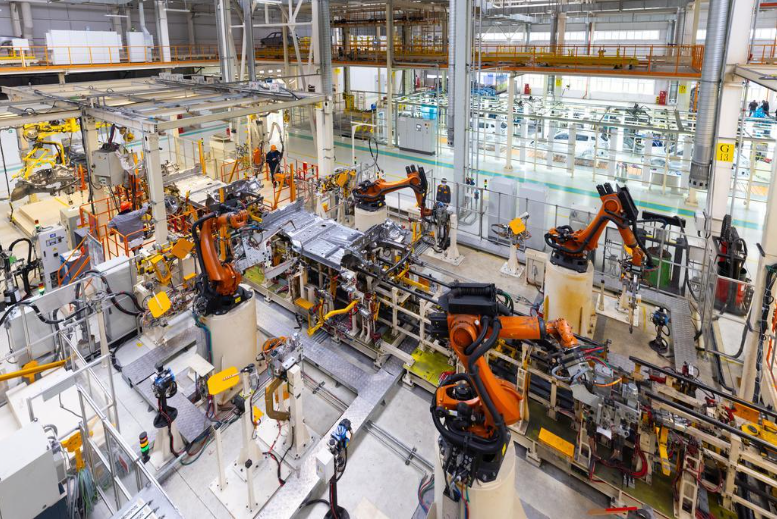

Overview of Vietnam’s manufacturing industry (Source)
Vietnam's manufacturing sector showcases resilience and strategic growth. Amid global uncertainties, the country has emerged as a key player in the international supply chain, driven by favorable policies, foreign investments, and technological advancements.
Why Vietnam Is a Global Manufacturing Hub
Vietnam's strategic location and competitive labor costs have positioned it as a prime destination for manufacturers. The country's participation in major trade agreements like the CPTPP and RCEP has opened access to markets representing over 30% of global GDP, reducing trade barriers and facilitating the flow of goods.
Key factors include:
- Competitive labor costs: The typical hourly wage in factories is around $2.99, which is much less than the $6.50 paid in China.
- Strategic location: Proximity to major Asian economies enhances its role in global trade.
- Government support: Tax incentives and infrastructure investments bolster the manufacturing environment.
Key Drivers of Growth in Vietnam’s Industrial Sector
Several elements contribute to the robust growth of the Vietnam industry:
- Foreign Direct Investment (FDI): In 2024, FDI disbursement reached approximately $25.35 billion, with manufacturing and processing leading at $25.58 billion.
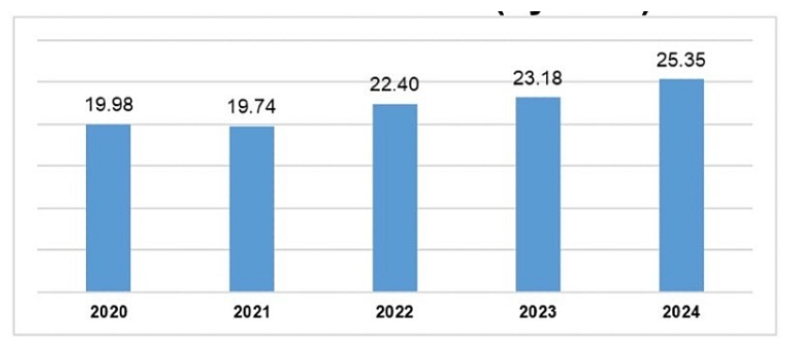
FDI disbursement (Source)
- Technological Advancements: The adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies, including automation and smart manufacturing, enhances productivity and positions Vietnam as a hub for innovative manufacturing solutions.
- Infrastructure development: Investments in transportation networks and logistics improve supply chain efficiency.
- Government Initiatives: Policies such as tax incentives for high-tech industries and the development of specialized industrial zones create a favorable business environment.
These factors collectively strengthen the Vietnam industry, making it more competitive globally.
Foreign Direct Investment and Trade Agreements Boosting the Industry
Vietnam's integration into global trade networks is a significant catalyst for its manufacturing sector. The country's active participation in FTAs reduces tariffs and operational costs for manufacturers, enhancing its global competitiveness.
Furthermore, the influx of FDI from major tech companies like Samsung, Microsoft, Intel, and LG underscores international confidence in Vietnam's manufacturing capabilities. These investments not only boost production capacity but also facilitate technology transfer and skill development within the Vietnam industry.
Key Sectors Powering Vietnam’s Manufacturing Industry
Vietnam's manufacturing sector is experiencing robust growth, positioning the country as a vital player in the global supply chain. Key industries such as textiles, electronics, automotive, and supporting sectors are driving this expansion, solidifying Vietnam's status as a manufacturing powerhouse.
Apparel and Textile Manufacturing in Vietnam

Textile manufacturing (Source)
Vietnam's textile and garment industry continues to thrive in 2025, bolstered by strong export demand and strategic trade agreements. The sector is projected to achieve exports between USD 50–52 billion this year, reflecting its resilience and adaptability to global market dynamics.
In the first quarter of 2025, the Vietnam National Textile and Garment Group (Vinatex) reported consolidated revenue of VND 4,417 billion, marking a 6.1% year-on-year increase. Compared to Q1 2024, profit soared by 165.5%, reaching VND 271 billion, reflecting solid performance in both spinning and garment units.
The industry's growth is further supported by key free trade agreements like the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP) and the EU-Vietnam Free Trade Agreement (EVFTA), enhancing competitiveness in major markets like the US, EU, and Japan.
Electronics and High-Tech Manufacturing in Vietnam

Electronics manufacturing (Source)
Vietnam's electronics manufacturing sector has become a cornerstone of its industrial landscape, contributing significantly to the national GDP. In 2023, the sector generated $115 billion in revenue, accounting for over a quarter of the country's GDP.
Major global corporations like Samsung and Intel have established substantial operations in Vietnam, attracted by competitive labor costs and a favorable investment climate. In 2024, foreign direct investment (FDI) in the manufacturing and processing industries reached approximately US$25.58 billion, with a significant portion directed towards electronics and high-tech manufacturing.
The sector's growth is also driven by Vietnam's strategic location in Southeast Asia, providing access to key markets and integration into global supply chains. This strategic location has turned Vietnam into a preferred choice for companies looking to expand their manufacturing locations.
Automotive and Auto Parts Manufacturing in Vietnam
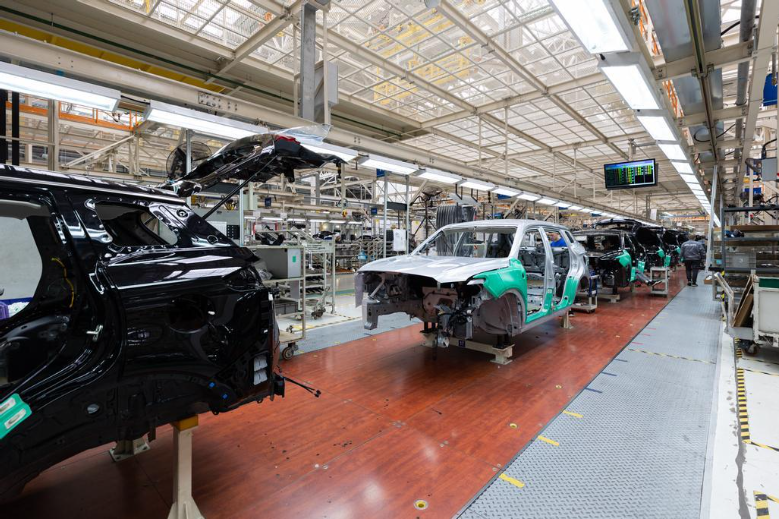

Automotive manufacturing (Source)
Vietnam's automotive industry is undergoing a significant transformation this year, emerging as a new hub for international car manufacturers. Domestic car production surged in the first months of 2025, with automobile output rising sharply compared to the same period last year. This growth is attributed to global carmakers selecting Vietnam as a destination for new manufacturing facilities.
In April 2025, car production in Vietnam reached approximately 39,500 units, marking a 60% increase compared to the previous year. From January to April, cumulative output reached 147,300 units, representing a 76.9% rise compared to the previous year.
Despite these advancements, the industry still faces challenges, such as low localization rates. In 2023, domestic assembly accounted for about 70% of vehicle sales, yet only 20% of the components were sourced from Vietnam, indicating a substantial dependence on foreign parts.
Supporting Sectors: Furniture, Footwear, and Food Processing
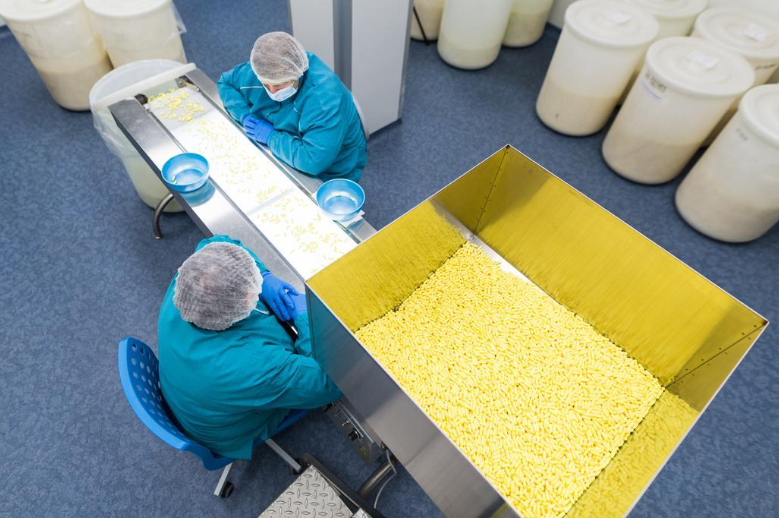

Food processing (Source)
Beyond the primary industries, Vietnam's manufacturing sector is bolstered by supporting industries like furniture, footwear, and food processing. These sectors contribute significantly to the country's economic growth and export performance.
- Furniture Manufacturing: Vietnam's furniture industry is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing global demand and competitive production costs. The sector's expansion is supported by the country's abundant natural resources and skilled labor force.
- Footwear Industry: Vietnam's footwear manufacturing industry increased by 1.9% in December 2024 compared to November 2024, according to the Industrial Production Index. Year-on-year, the sector posted robust growth of 23.5% in December 2024 compared to December 2023. For the full year of 2024, cumulative growth reached 13.7% compared to 2023, highlighting strong performance throughout the year.
- Food Processing: The food processing industry in Vietnam is expanding, supported by rising domestic consumption and export opportunities. The sector benefits from the country's rich agricultural resources and increasing investments in processing technologies.
These supporting sectors enhance the diversity and resilience of Vietnam's manufacturing industry, contributing to its overall competitiveness in the global market.
Vietnam’s Competitive Advantages in Manufacturing

Competitive advantages in manufacturing (Source)
The manufacturing sector in Vietnam has become a major global player, thanks to strategic benefits that appeal to international businesses and investors. These strengths position the Vietnam industry as a key player in the global supply chain.
- Cost-Effective Labor: Vietnam’s workforce offers cost advantages, featuring monthly wages significantly cheaper than those in neighboring countries. This affordability makes it an attractive destination for labor-intensive manufacturing.
- Strategic Location: Situated in Southeast Asia, Vietnam provides easy access to major markets like China, Japan, and South Korea. Its proximity to global shipping routes enhances its appeal for export-oriented manufacturing.
- Robust Trade Agreements: Vietnam's participation in multiple free trade agreements, including the CPTPP and EVFTA, facilitates tariff reductions and market access, boosting its manufacturing exports.
- Growing Infrastructure: Continuous investments in infrastructure, such as industrial parks and transportation networks, support the expansion of the Vietnam industry.
These factors collectively enhance Vietnam's manufacturing competitiveness, making it a preferred choice for global businesses seeking efficient and cost-effective production solutions.
Challenges Facing Vietnam’s Manufacturing Industry

Challenges facing Vietnam’s manufacturing industry (Source)
While Vietnam’s manufacturing has seen substantial growth, it still confronts issues that might affect its future progress:
- Infrastructure Limitations: Rapid industrial expansion has outpaced infrastructure development, leading to congestion and inefficiencies in transportation and logistics. This bottleneck hampers the smooth flow of goods and materials, affecting overall productivity.
- Trade Policy Uncertainties: The imposition of new tariffs by major trading partners, such as the United States, has introduced volatility into Vietnam's export markets. These tariffs, ranging between 32% and 49%, particularly impact the electronics and apparel sectors, prompting companies to reassess their production strategies.
- Labor Market Challenges: While Vietnam offers a cost-effective labor force, there is a growing need for skilled workers to meet the demands of high-tech manufacturing. The shortage of adequately trained personnel could hinder the sector's move up the value chain.
To ensure sustainable growth, the Vietnam industry must address these challenges through strategic investments in infrastructure, workforce development, and adaptive trade policies.
Kizuna: A Strategic Partner for Manufacturers in Vietnam
In the rapidly evolving Vietnam industry, partnering with a reliable logistics and supply chain expert is key to success. Kizuna stands out as a trusted partner for manufacturers seeking efficient, integrated solutions in Vietnam.
Kizuna offers multiple advantages that make it a top choice for businesses operating in Vietnam’s manufacturing sector:
- Comprehensive Supply Chain Solutions: Kizuna provides end-to-end logistics services, covering warehousing, freight forwarding, and customs clearance, ensuring smooth operations.
- Local Expertise with Global Standards: The company combines deep knowledge of Vietnam’s market with international best practices, helping clients navigate complex regulations.
- Advanced Technology Integration: Use of digital tools enhances real-time tracking, inventory management, and process transparency.
- Strong Network and Infrastructure: Kizuna’s extensive connections with ports, transporters, and warehouses accelerate delivery and reduce costs.
- Sustainability Commitment: Focus on green logistics aligns with global trends and client expectations for environmental responsibility.
- Customer-Centric Approach: Tailored solutions meet specific manufacturing needs, boosting operational efficiency and competitiveness.
- Proven Track Record: Successful partnerships with major brands demonstrate reliability and consistent service quality.
Kizuna’s capabilities make it a key enabler for growth in the Vietnam industry, helping manufacturers overcome logistical challenges and maximize their potential.